How Long To Recover From Miniscus Repair And Clean Up Bone And Artharitus In Knee
Description of a Lateral Meniscus
The lateral meniscus is an essential daze absorber on the exterior (lateral) aspect of the human knee articulation. It absorbs near 70% of the shock of the lateral compartment. Lateral meniscal tears are not as common as medial meniscus tears. This is because the lateral meniscus is more than mobile and non secured as much to the lateral tibial plateau equally the medial meniscus is to the medial tibial plateau. Thus, when in that location is a lateral human knee injury such every bit a lateral meniscus tear, information technology is very of import to try to repair the tear, considering if not repaired and is trimmed out there will be an increase to the load on the lateral compartment, which ultimately leads to osteoarthritis.
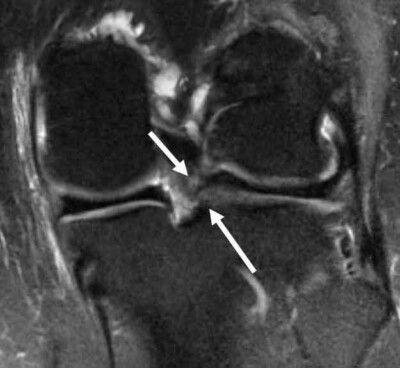
Coronal MRI scan demonstrating a posterior horn lateral meniscus blazon Ii root tear. The lateral meniscus root is torn upward to 12% of the time concurrently with an ACL tear. Failure to recognize this tear pattern can lead to failure of the ACL reconstruction graft due to increase in stress with both anterior translation of the knee joint and for internal rotation during the pivot shift.
CLICK Image TO Overstate
Symptoms of a lateral meniscus tear:
- Pain
- Swelling and stiffness, increases gradually from hours to days afterward injury
- Catching or locking
- Instability
- An disability to straighten the knee
Treatment of a Lateral Meniscus Tear
Due to the added shock arresting capacity of the lateral meniscus, it is essential to effort to repair lateral meniscus tears if possible. Nosotros believe that trying to stimulate an improved healing environment through the use of bone marrow elements, platelet rich plasma (PRP), and a large number within-out meniscal repair sutures, can lead to improved ability to heal these tears, particularly in younger patients.
Mail-Op
The handling for patients who undergo a fractional lateral meniscectomy is to initiate physical therapy on the offset 24-hour interval after surgery. A handling regimen working on reactivation of the quadriceps muscles, regaining of full genu and patellar mobility, and a quick resolution of knee joint swelling is emphasized. In full general, nosotros recommend that patients who have a minimal amount of lateral meniscus trimmed out concord back on any impact activities until a minimum of half dozen weeks after surgery. In patients who have a significant corporeality of meniscus resected, it is often recommended to avert significant touch activities due to the higher risk of the development of osteoarthritis in these patients with this activity.
When a torn lateral meniscus needs to be resected, we strongly recommend that these patients be followed very closely. Patients demand to report dorsum to their physician if they take whatever pain or swelling with activities, because these are the signs of arthritis and may point farther progression of arthritic changes. If this is present, further treatment to include activity modification, low impact exercising, unloader braces, injections, or possible meniscal transplantation may be indicated.
It is almost inevitable that when one has a significant corporeality of the lateral meniscus resected that they will develop further arthritic changes over time. Considering not everybody is the same, these changes can develop within a few weeks up to over a decade. Nosotros take observed that this oftentimes can develop rapidly in younger patients. Thus, one of the important things is to recognize that if one has any pain or swelling, they should follow up to make sure they are non developing any joint infinite narrowing or bone spurs, which would betoken that the lateral compartment articular cartilage is wearing out.
Lateral Meniscus Tears FAQ
The lateral meniscus is about a C-shaped cushion on the exterior of i's knee. The lateral meniscus absorbs up to 70% of the shock, on average, that is placed across the lateral compartment of the knee joint. Therefore, the lateral meniscus is very important to preserve when it is torn because in that location is a very loftier risk of progression of arthritis if a meniscus is not repaired.
one. Can a lateral meniscus tear heal itself?
There are some types of lateral meniscus tears that could potentially heal themselves. They depend upon the type of meniscus tear and the location of the tear in the joint. If the meniscus is torn at the border where it attaches to the joint lining and the tear is small, there is the possibility this could heal. In addition, there accept been occasional case reports that report that some radial tears may heal over time, although this is not expected for the vast bulk of tears. What it does indicate is that the lateral meniscus does have some power to heal, and so pushing the limits for a repair, especially in a young patient, would be indicated.
2. Where does the knee hurt when there is a lateral meniscus tear?
In general, a lateral meniscus tear should cause hurting forth the joint line of the outside part of the knee. In addition, one could take hurting in the back of their knee with deep squats or they could take pain on the outside of their knee joint when they put their leg in a figure-of-iv position. These are the usual locations that a lateral meniscus tear will hurt.
3. Is the lateral meniscus tear worse than a medial meniscus tear?
It is hard to differentiate what blazon of tear is worse if information technology is repairable. However, it is well known that if a lateral meniscus is taken out, the consequences are almost e'er worse than having a medial meniscus resected.
iv. What does a circuitous lateral meniscus tear mean?
A complex lateral meniscus tear can include a radial tear, a radial flap tear, a tear that is chewed upward and diminished, or a root tear. In general, a simpler type tear would exist one that is very small and trimmable or ane that is torn at the meniscus attachment to the joint lining, which is easily repairable.
5. How does one treat a lateral meniscus tear?
In full general, because of the important daze-absorbing ability of the lateral meniscus, repairable lateral meniscus tears should have an attempt at a repair equally long as the patient is fairly active and does not have any significant arthritis. For smaller tears or tears that are in an area with hardly whatsoever blood supply, a trimming would possibly exist indicated. This would be called a partial lateral meniscectomy.
6. What type of cysts are those that develop with a lateral meniscus tear?
Sometimes a lateral meniscus will have a split in the center, called a horizontal tear, whereby fluid tin can leak out through the joint lining. This fluid tin can accumulate over time and almost be a jelly-like substance. This is chosen a lateral meniscal cyst or a parameniscal cyst. In about circumstances, the cyst is caused by the meniscus tear. Therefore, when one does excise the cyst, the meniscus tear needs to exist addressed, most commonly by suturing the meniscus tear to prevent the cyst from reforming.
7. What does 1 do tor the lateral meniscus tear when one has osteoarthritis?
The osteoarthritis amount would determine what type of handling may be indicated for a lateral meniscus tear. If at that place is very minimal arthritis and the meniscus is repairable, a repair should exist performed. However, if in that location is bone-on-bone arthritis and in that location is a tear present, unless at that place is a definitive mechanical problem, limiting one's function, and observation, rather than a partial meniscectomy may be indicated.
8. How does i treat an inductive horn lateral meniscus tear?
Anterior horn lateral meniscus tears are harder to treat technically because the surgical instruments that have been developed are not as skilful at addressing these tears. For trimmable tears, using a curved shaver or an arthroscopic device that bites astern, called a backbiter, may be indicated. If in that location is a tear of the meniscus that is repairable, using a technique called the exterior-in technique would be advisable to perform a straight repair of the anterior horn lateral meniscus tear.
9. How often are lateral meniscus tears missed on MRI?
In our practice nosotros find that MRI is much more successful at diagnosing medial meniscus tears compared to lateral meniscus tears. In the literature, the lateral meniscus tear diagnosis via MRI has been reported to be between fourscore% to ninety% successful. Thus, information technology is entirely possible that i could go into surgery thinking that the lateral meniscus is okay and a further evaluation and probing may reveal a large tear that was non picked up on the MRI browse.
x. What does one do to a lateral meniscus tear with extrusion?
Extrusion can be due to two things. One could be that the cartilage is worn out and the meniscus is being squirted out of the joint because of the amount of arthritis. The second could exist that there is a radial root tear of the lateral meniscus which is causing it to slip out of the joint. Radial or lateral meniscus root tears should be repaired if the cartilage surfaces are still pretty adept. This involves releasing scar tissue and pulling the meniscus back in the articulation and so either suturing it together or tacking it back downward to os, depending upon the type of tear.
xi. What is a lateral meniscus tear in the ruddy zone?
Meniscus tears are classified according to the distance from the articulation lining, which is almost directly proportional to the blood supply that is present. Within the first 2-iii mm there is a good blood supply, so tears in this zone we call red-carmine. Tears that are two-3 mm abroad from this are more at the edge of the red zone and into the white zone where in that location is less blood supply and we will call these red-white tears. Tears that are farther along, more than 6 mm from the edge, are more at an area where in that location is poor blood supply and these are called white-white zone tears. More recent literature suggests that the meniscus does have a good ability to heal itself with white-white zone tears, and so repairs of large tears in this zone would be recommended.
12. How does ane differentiate between a lateral meniscus tear and iliotibial band friction syndrome?
1 of the best means to differentiate between a lateral meniscus tear and iliotibial ring friction syndrome is performing a skillful history and concrete examination on a patient. In general, iliotibial band friction syndrome develops over fourth dimension with activity, usually afterward a runner has been running up to 2 miles and does not hurt initially. Meniscus tears that are catching the joint would exist expected to hurt every bit shortly as 1 started to run. In addition, meniscus tears should exist painful at the articulation line, whereas a tight iliotibial band would unremarkably hurt when 1 pushes directly over the lateral epicondyle and flexes and extends the knee. The iliotibial band that may be irritated with the iliotibial band friction syndrome should be painful with this maneuver if i pushes down hard enough on the lateral epicondyle.
xiii. Can a lateral meniscus tear cause a Baker'due south cyst?
A Baker's cyst is a fluid pocket that develops when fluid leaks out the back of the inside role of the knee between the medial caput of the gastrocnemius and the direct arm of the semimembranosus. Most of u.s. have a little hole in the back of our knees at dislocation. Thus, anything that could cause swelling in the genu tin upshot in a Baker's cyst forming. Thus, if a lateral meniscus does cause some swelling, it can lead to the development of a Baker's cyst. The treatment for a Baker'south cyst is to treat the problem at the front of the articulatio genus and other than very rare occasions, surgery to treat a Baker's cyst is not performed.
14. Can stem cell handling heal a lateral meniscus tear?
At that place are many different types of lateral meniscus tears with the importance depending on the size of the tear, the location in terms of blood supply, and its duration. For large flaps of meniscus tears or meniscus root tears which accept separated, a os marrow aspirate injection or a true stalk cell injection, which are non allowed in the U.S. and mainly performed in Europe or Republic of chile, would take a low chance of working. We exercise know that bone marrow injections can make a knee less irritated, simply the chance of healing a tear in this circumstance would exist minimal. For meniscus tears that do take a loftier potential of healing on their own, such as small tears at the meniscocapsular junction, information technology is theoretically possible that the bone marrow injections, which are unremarkably called "stalk cell injections" in the Us, could potentially lead to their healing. Nevertheless, larger tears would still be suited to having a repair and possible augmentation with bone marrow aspirate.
15. What is a lateral meniscus free-edge tear?
If ane slices through a meniscus, it is shaped like a triangle. The inner portion of the triangle that is thinner is only like the inner portion of the meniscus. This would be the free-edge tear. At this location the meniscus may only be ane mm to 2 mm in total depth, so an try at a repair would not exist indicated. In near of these small free-edge tears, trimming them carefully to remove the surface area of the tear, but not remove whatsoever further tissue, would be indicated.
16. What should one do with a lateral meniscus tear in a teenager?
Considering of the severe consequences of taking a lateral meniscus out in a teenager, which almost always leads to the evolution of osteoarthritis within 1-ii decades, it would be recommended to perform a repair if possible. Many complex tears may be suitable to attempted repairs at this historic period group because of their better healing potential and as well may benefit from biologic augmentation with a marrow venting procedure, bone marrow injection, or a leukocyte-poor PRP injection to augment the healing process.
17. What causes locking with a lateral meniscus tear?
1 of the most common causes of locking with a lateral meniscus tear are either a tear that has torn at the edge and slips into the joint with twisting and turning or a meniscus that totally flipped from the back to the front, called a bucket-handle tear, which tin can block extension. Many athletes that are seen that do present with a a bucket-handle tear had a previous history of communicable or locking with activities that was a prelude to having the entire meniscus flip upon itself.
18. What can exist done for a horizontal lateral meniscus tear?
Horizontal lateral meniscus tears can be repaired and this could be considered in younger patients. In older patients who have symptoms, removing the inferior leaf of the tear and preserving the superior leaf to endeavor to serve as stupor assimilation would be recommended. We do know that removing half of the meniscus definitely increases the risk of arthritis, merely it would be better than removing the whole meniscus. A horizontal meniscus repair would involve cleaning out between the two upper and lower portions of the meniscus with a shaver, suturing the top and the lesser together, and consideration of inserting a fibrin clot betwixt the 2, like a peanut butter and jelly sandwich, to try to deliver the maximum corporeality of growth factors into the expanse of the tear to try to maximize healing.
19. What should be the handling for a lateral meniscus bucket-handle tear?
Because the lateral meniscus is so important for shock absorbing, one should attempt to have a repair of the lateral meniscus when possible and when ane does not have any significant arthritis. This would involve an arthroscopy to push the meniscus back in place and using multiple sutures to hold the meniscus in place. The gold standard for this would exist an inside-out repair with multiple sutures, varying anywhere from 10-twenty full number of sutures.
20. What causes a lump forth the articulation line with a lateral meniscus tear?
The most common cause of a lump with a lateral meniscus is a lateral meniscus cyst at the joint line. Small lumps can occur from a fragment of the meniscus being displaced forth the joint line or under the meniscus and along the capsule, which can sometimes exist palpable and painful.
Have you sustained a lateral meniscus tear?
In that location are two ways to initiate a consultation with Dr. LaPrade:
Yous tin provide current 10-rays and/or MRIs for a clinical case review with Dr. LaPrade.
Yous can schedule an role consultation with Dr. LaPrade.
Source: https://drrobertlaprademd.com/lateral-meniscus-tear/
Posted by: mosbybress1948.blogspot.com



0 Response to "How Long To Recover From Miniscus Repair And Clean Up Bone And Artharitus In Knee"
Post a Comment